by Kerry McDonald
There are mounting concerns over profound learning loss due to prolonged school closures and remote learning. New data released last week by the US Department of Education reveal that fourth-grade reading and math scores dropped sharply over the past two years.
Fingers are waving regarding who is to blame, but the alleged “learning loss” now being exposed is more reflective of the nature of forced schooling rather than how children actually learn.
The current hullabaloo over pandemic learning loss mirrors the well-worn narrative regarding “summer slide,” in which children allegedly lose knowledge over summer vacation. In 2017, I wrote an article for Boston NPR stating that there’s no such thing as the summer slide.
Students may memorize and regurgitate information for a test or a teacher, but if it has no meaning for them, they quickly forget it. Come high school graduation, most of us forget most of what we supposedly learned in school.
In his New York Times opinion article this week, economist Bryan Caplan makes a related point: “I figure that most of the learning students lost in Zoom school is learning they would have lost by early adulthood even if schools had remained open. My claim is not that in the long run remote learning is almost as good as in-person learning. My claim is that in the long run in-person learning is almost as bad as remote learning.”
Learning and schooling are completely different. Learning is something we humans do, while schooling is something done to us. We need more learning and less schooling.
Yet, the solutions being proposed to deal with the identified learning loss over the past two years promise the opposite. Billions of dollars in federal COVID relief funds are being funneled into more schooling and school-like activities, including intensive tutoring, extended-day learning programs, longer school years, and more summer school. These efforts could raise test scores, as has been seen in Texas where students receive 30 hours of tutoring in each subject area in which they have failed a test, but do they really reflect true learning?
Certainly, many children have been deprived of both intellectual and social stimulation since 2020, as lockdowns and other pandemic policies kept them detached from their larger communities. I wrote back in September 2020 that these policies were damaging an entire generation of kids, and urged parents to do whatever possible to ensure that their children had normal interactions with the wider world.
Children who were not able to have those interactions will need more opportunities now to play and explore and discover their world. It is through this play, exploration, and discovery that they will acquire and expand their intellectual and social skills. This is best facilitated outside of a conventional classroom, not inside one.
“What we need is less school, not more,” writes Boston College psychology professor Peter Gray. “Kids need more time to play and just be kids. Mother nature designed kids to play, explore, and daydream without adult intervention because that is how kids develop the skills, confidence, and attitudes necessary for mental health and overall wellbeing.”
Fortunately, non-coercive schooling alternatives are becoming more widely available. My latest Forbes article describes an Illinois public middle school science teacher, Josh Pickel, who quit his job this summer to open a new self-directed microschool. As Pickel wondered: “What if we removed coercion and those kids were allowed to focus their energy and their intellect on things they care about?”
The start of this new school year brings with it greater education possibilities, including those like Pickel’s that enable children to joyfully explore content they care about, in pursuit of goals that matter to them, leading to genuine learning retained for years to come.
We can criticize school shutdowns and affirm that they never should have happened, while also recognizing that imposing more schooling is not the solution to presumed pandemic-era learning loss. It might raise test scores, but it’s unlikely to lead to true learning. Only freedom can do that.
– – –
Kerry McDonald is a Senior Education Fellow at FEE and host of the weekly LiberatED podcast. She is also the author of Unschooled: Raising Curious, Well-Educated Children Outside the Conventional Classroom (Chicago Review Press, 2019), an adjunct scholar at the Cato Institute, education policy fellow at State Policy Network, and a regular Forbes contributor. Kerry has a B.A. in economics from Bowdoin College and an M.Ed. in education policy from Harvard University. She lives in Cambridge, Massachusetts with her husband and four children.
Photo “Teacher and Students” by 14995841.
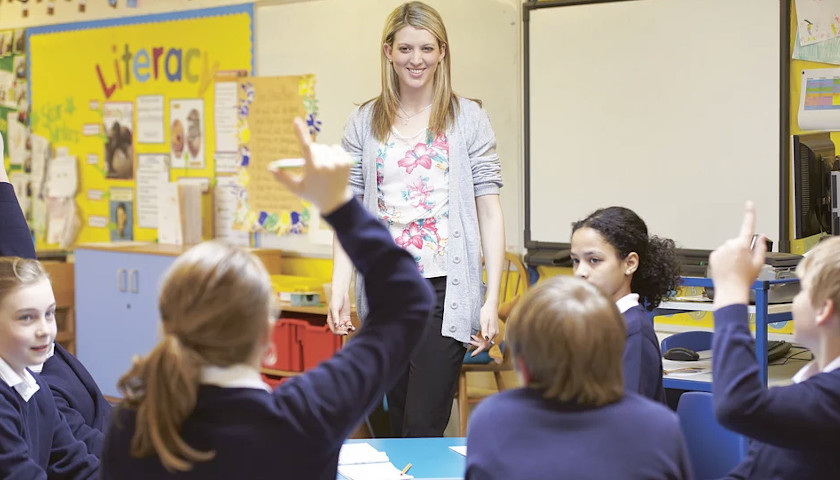








Children cant learn multiplication tables or basic methods of adding and subtraction without the teacher telling them how to do it. The same applies to units of measuring distance or volume.